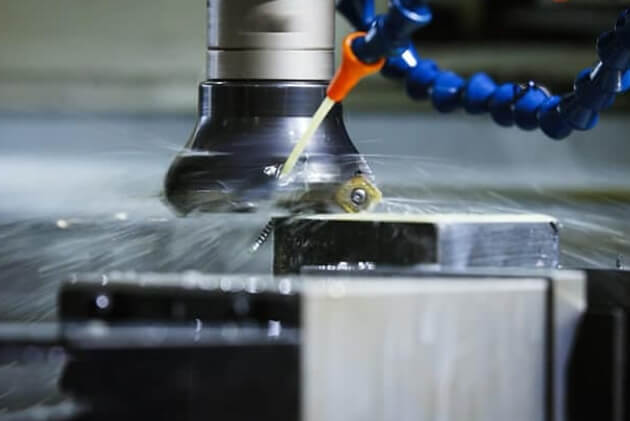
Classification of Mold Steels Based on Purpose and Application
Manufacturing mold steels are diverse, adhering to standards from the United States, Germany, Japan, and national standards. They can be classified based on the intended use of the mold into cold work mold steel, hot work mold steel, plastic mold steel, etc. Each standard has different designations and codes.
- Cold Work Mold Steel:
Cold work mold steel is primarily used for manufacturing molds that exert pressure on workpieces in a cold state. Examples include cold cutting dies, cold stamping dies, cold drawing dies, embossing dies, cold extrusion dies, thread pressing dies, and powder metallurgy dies.
The range of cold work mold steel is extensive, spanning from various carbon tool steels, alloy tool steels, high-speed tool steels to powder metallurgy high-speed tool steels and powder metallurgy high-alloy mold steels.
- Hot Work Mold Steel:
Hot work mold steel is employed in manufacturing molds that exert pressure on workpieces in a high-temperature state. Examples include hot forging dies, hot extrusion dies, die-casting molds, and hot upsetting dies.
Commonly used hot mold steels include alloy mold steels containing elements such as Cr, W, Mo, V; and, in some cases, special requirements lead to the use of high-alloy austenitic heat-resistant mold steels.
- Plastic Mold Steel:
Due to the wide variety of plastics and the varying requirements for plastic products, there is a diverse series of plastic mold steels in many industrialized countries.
This series encompasses carbon structural steel, carburizing plastic mold steel, pre-hardened plastic mold steel, age-hardening plastic mold steel, corrosion-resistant plastic mold steel, easy-cutting plastic mold steel, fully hardened plastic mold steel, martensitic age-hardening steel, and mirror-polished plastic mold steel, among others.