Differences in Parts Used for Stamping Dies and Injection Molds
Introduction: Stamping dies and injection molds are crucial tools in the manufacturing industry, each designed for specific processes. One key aspect that sets them apart is the type of parts used in their construction. This article explores the differences in the components employed in stamping dies and injection molds.
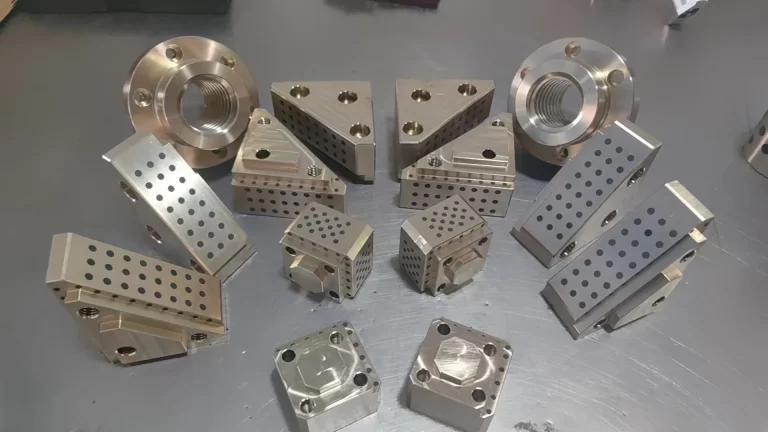
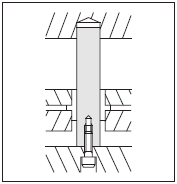
Stamping Dies: Stamping dies are primarily used in metal forming processes to cut, shape, or deform materials such as sheet metal. The key components of stamping dies include:
- Die Block: The main supporting structure of the die that holds other components in place.
- Punch: A tool that applies force to the material, causing it to deform or cut.
- Die Cavity: The recessed area where the material is shaped or cut.
- Strippers: Components that help remove the formed material from the punch.
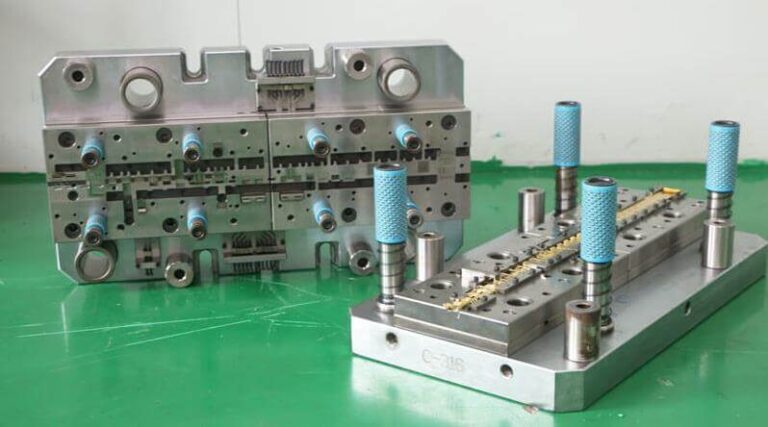
Injection Molds: Injection molds, on the other hand, are utilized in the plastic manufacturing process, injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity. The main parts of injection molds include:
- Mold Base: The primary supporting structure that holds all other components in place.
- Core and Cavity: The mold’s main components, defining the shape of the final product.
- Sprue Bushing: The entry point for molten plastic into the mold cavity.
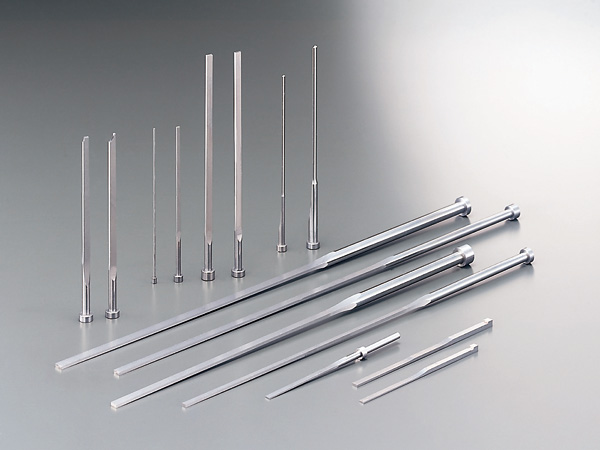
- Ejector Pins: Components that push the finished product out of the mold after cooling.
Differences in Parts: While there are some similarities in the terminology used for components, the materials and designs of these parts differ based on the unique requirements of stamping dies and injection molds.
- Material: Stamping dies often use hardened steel or other robust materials to withstand the force applied during metal forming. Injection molds, dealing with molten plastic, require materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures, such as tool steel or aluminum.
- Functionality: The components in stamping dies are geared towards cutting, shaping, and forming metal sheets. In contrast, injection molds focus on facilitating the flow of molten plastic and creating the desired shape for the final product.
- Wear Resistance: Stamping dies face wear due to constant metal-on-metal contact, requiring components with high wear resistance. Injection molds need materials that resist wear caused by the abrasive nature of molten plastic.