Nitrogen Gas Springs: The Elastic Choice for Industrial Applications
Nitrogen Gas Springs are components that utilize high-pressure nitrogen gas sealed within a container to provide spring force. They are widely used in industrial fields. Below is an article about the applications of nitrogen gas springs
Working Principle of Nitrogen Gas Springs
Nitrogen gas springs work by sealing high-pressure nitrogen gas within a specific container. When an external force acts on the piston rod, the nitrogen gas is compressed, generating spring force. Once the external force is removed, the nitrogen gas expands, providing a reverse force. This design enables nitrogen gas springs to generate a large force in a small space while maintaining force stability.
Applications of Nitrogen Gas Springs
Mold Industry
Nitrogen gas springs simplify the structure in mold design, enhancing the adjustability and ease of use of molds. They can be installed as independent components or designed as part of a system to achieve constant spring force and delayed actions.
Comparison: Nitrogen Gas Springs vs. Metal Springs
| Comparison | Nitrogen Gas Springs | Metal Springs |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | High-pressure nitrogen gas is filled in a sealed container, achieving compression and release through pressure changes. | Elastic force is generated by the bending or twisting of elastic materials. |
| Force Stability | The force remains nearly constant throughout the entire stroke. | The force varies with the stroke and may exhibit nonlinear changes. |
| Space Occupation | Generates a large force in a small space. | Usually requires a larger space to generate the corresponding force. |
| Adjustability | The force magnitude and point of application can be adjusted at any time. | Poor adjustability, typically requires different specifications for adjustment. |
| Lifespan | Long service life, up to 2 million cycles or one year. | Relatively shorter lifespan, significantly affected by fatigue. |
| Installation and Maintenance | Easy to install and maintain. | Installation can be complex, with relatively high maintenance requirements. |
| Application Flexibility | Can be designed as independent components or integrated systems. | Lower application flexibility, limited by spring specifications. |
| Force Range | Can provide forces ranging from a few kilograms to several tons. | Limited force range, constrained by material and size. |
| Manufacturing Cost | Relatively high initial investment. | Lower manufacturing cost. |
| Adaptability | Suitable for various complex mold structures. | General adaptability, may require additional structural support. |
Automotive Industry
Compared to regular molds, automotive molds have a greater need for nitrogen gas springs. This is particularly true for molds used in stamping cover parts, which are often large in size, complex in shape, and require high precision.
Additionally, the materials used in stamping have high hardness. Nitrogen gas springs can generate a large force within a small space, which is especially beneficial for automotive mold designs where space is limited.
Electronics Industry
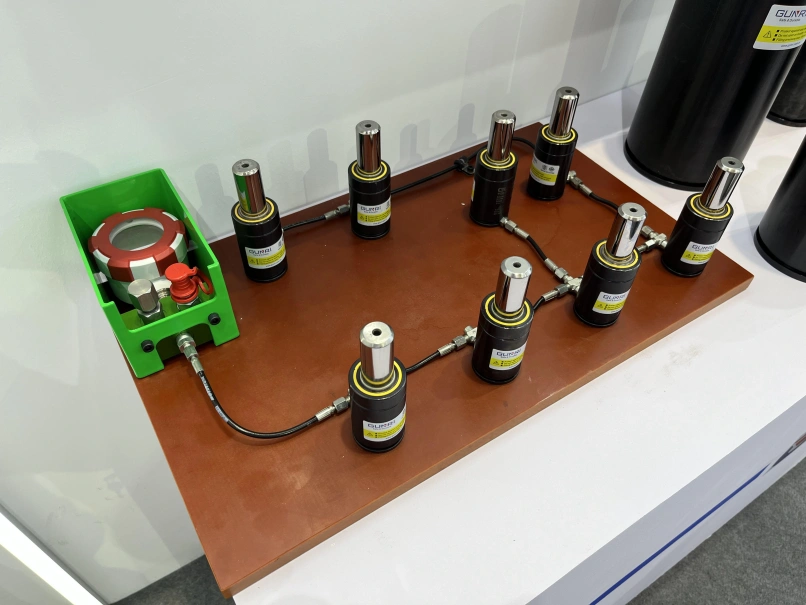

Due to their straight force curves, uniform strength variation, long lifespan, large stroke, and stable, reliable operation, nitrogen gas springs are effectively used in molds for producing electronic components. They can significantly reduce the closed height (with compression typically ranging from 50% to 60% of the gas spring’s length).
Additionally, their ability to exert high individual pressure makes them particularly suitable for use in confined mold spaces.
Computer Hardware
In the forming process of components such as computer drive housings, the use of nitrogen gas springs improves forming quality and resolves issues during the drawing process.
Nitrogen gas springs can also be applied in other industries and need to be specially customized according to different usage scenarios. You can contact GUNRI for expertise in this area. GUNRI has provided high-quality and precise mold components to various countries. For further information, please contact us.







