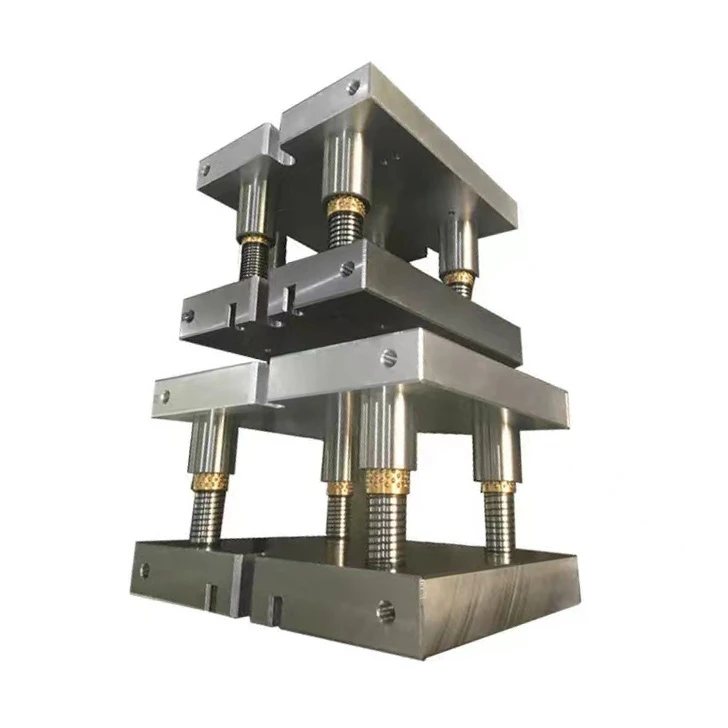
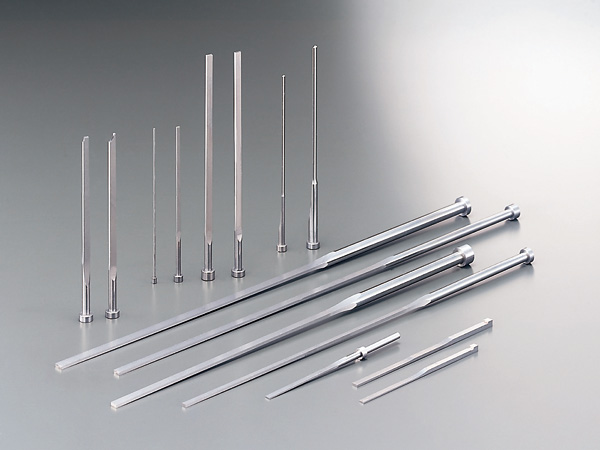
Why Choose Aluminum Ball-Bearing Guide Bushings Over Plastic in Stamping Die Applications?
In stamping die manufacturing, the selection between aluminum and plastic ball-bearing guide bushings depends on specific operational requirements and environmental conditions. Below are key factors that justify the use of aluminum guide bushings in certain scenarios:
1. Lightweight Design with Enhanced Strength
- Plastic Bushings: Lightweight and cost-effective but limited in strength and rigidity. They are prone to deformation or wear under sustained loads.
- Aluminum Bushings: Slightly heavier than plastic but offer superior mechanical strength and rigidity. Ideal for applications requiring lightweight solutions while enduring moderate to high stress, such as high-frequency die operations or precision tooling.
2. Thermal Management
- Aluminum’s thermal conductivity (~237 W/m·K) is approximately 1,000 times higher than most plastics. In high-speed stamping or continuous production cycles, aluminum bushings efficiently dissipate heat, preventing thermal expansion or softening—common issues with plastic components. This ensures dimensional stability and prolongs die life.
3. Wear Resistance and Durability
- Aluminum bushings can undergo surface treatments like anodizing or hard-coating to significantly improve wear resistance. This makes them suitable for high-frequency, long-term operations where plastic bushings would degrade rapidly. Reduced maintenance and longer replacement intervals further lower total ownership costs.
4. Corrosion Resistance
- Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, offering better resistance to moisture, lubricants, and mild chemicals compared to unmodified plastics. This is critical in humid environments or applications involving coolants or oils.
5. Cost-Effective Machinability
- Aluminum is easier to machine into complex geometries than stainless steel, making it a cost-effective choice for custom designs. Unlike plastic injection molding (which requires expensive tooling), aluminum machining suits low-to-medium production volumes while maintaining precision.
6. Specialized Applications
- Aluminum is non-magnetic, making it ideal for dies integrated with magnetic sensors or actuators. It also provides electrical and thermal conductivity when needed for grounding or heat transfer.
Real-World Example:
In household product manufacturing (e.g., stamping stainless steel thermos cups), aluminum bushings are preferred for high-speed production lines. They withstand rapid cycling and heat buildup, whereas plastic bushings might warp or wear prematurely, compromising precision.
Conclusion:
Aluminum ball-bearing guide bushings outperform plastic in scenarios demanding balanced strength, thermal stability, durability, and corrosion resistance. They are ideal for medium-to-high load applications, high-temperature environments, or extended production runs. Plastic remains viable for low-cost, low-stress, or short-term uses. Material selection should align with operational priorities, lifecycle costs, and environmental conditions to optimize die performance and economy.